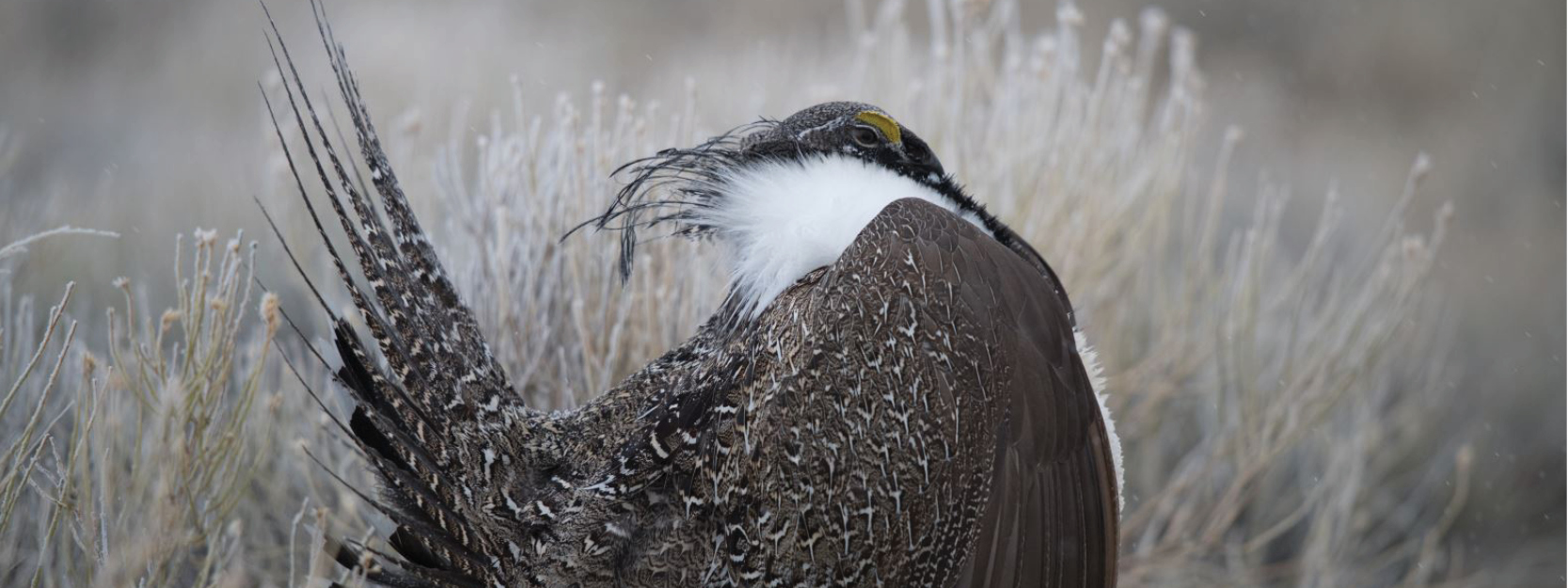
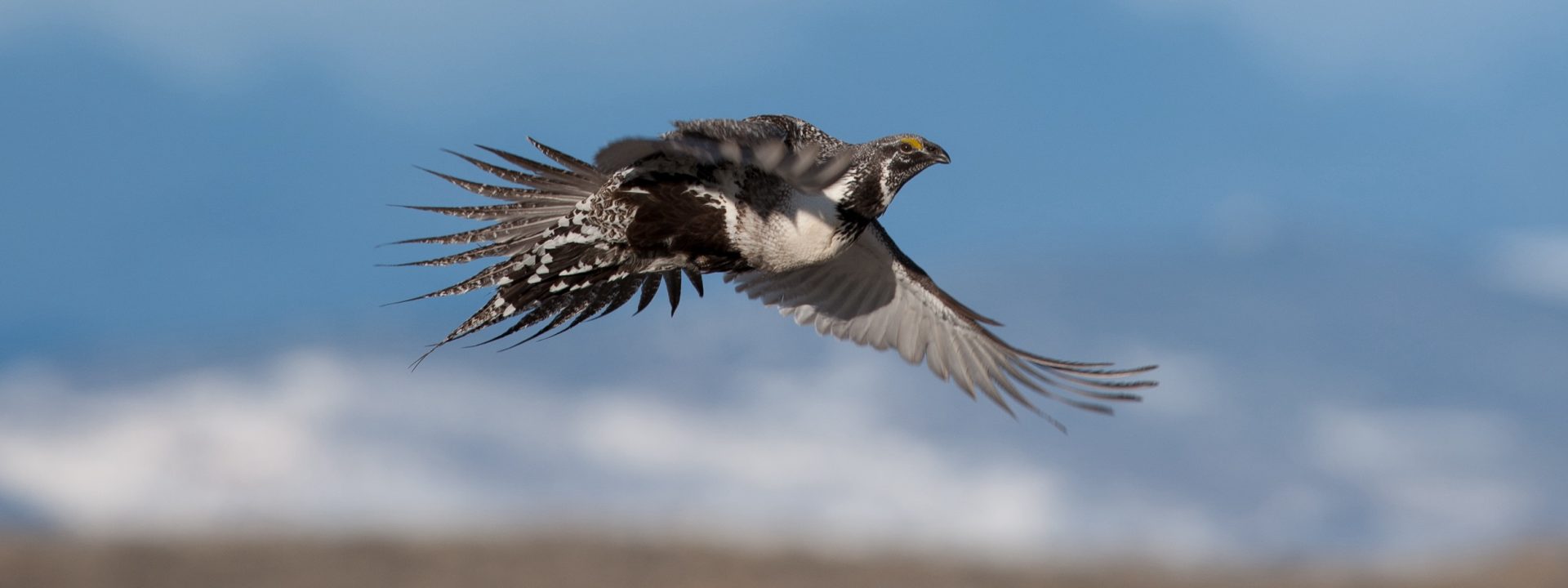
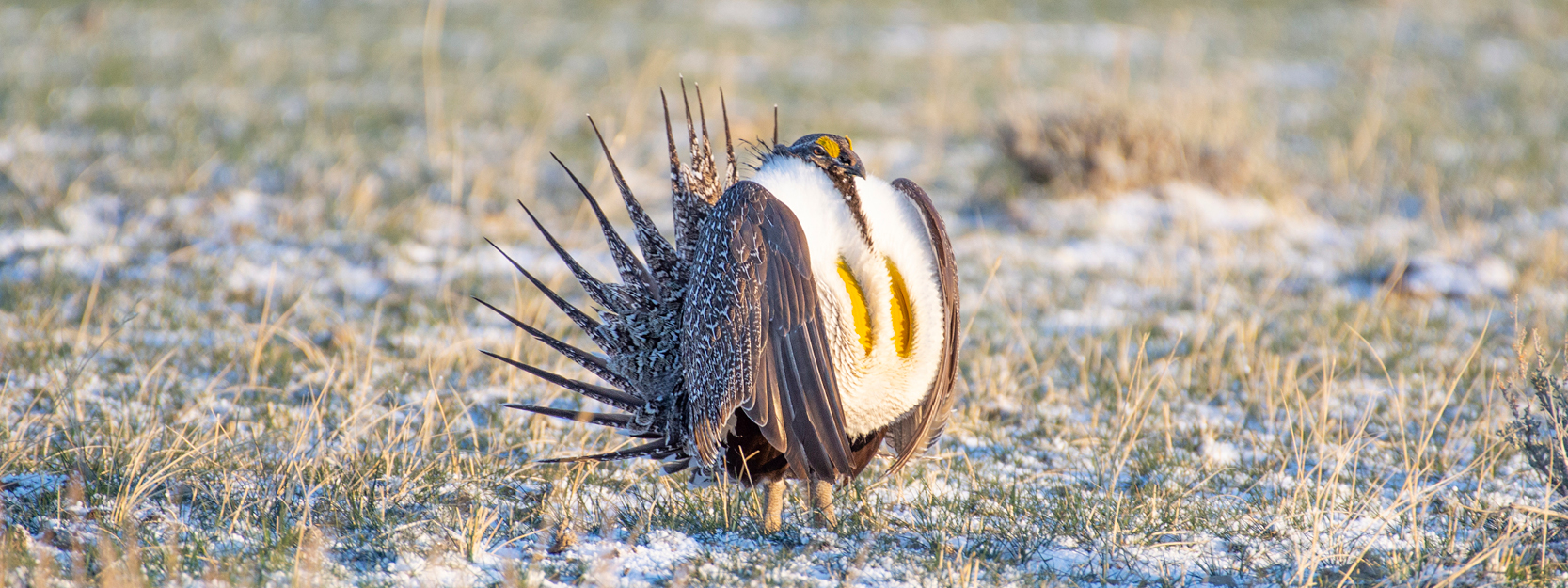
This month, the Bureau of Management unveiled its new plan for Greater sage-grouse. With the plan comes a ray of hope — both for the imperiled bird and the ever-diminishing sagebrush steppe ecosystem it depends on. Since the BLM manages more sage-grouse habitat than any other entity, actions taken on these public lands will have massive impacts across the West. The BLM’s final Greater Sage-Grouse Resource Management Plan Amendments serve as a new blueprint for how the agency will manage sagebrush habitat on behalf of sage-grouse, other wildlife, and a slew of other uses. What remains to be seen is if we can muster the political will to make this plan a reality and address the very real challenges facing an ecosystem in distress.
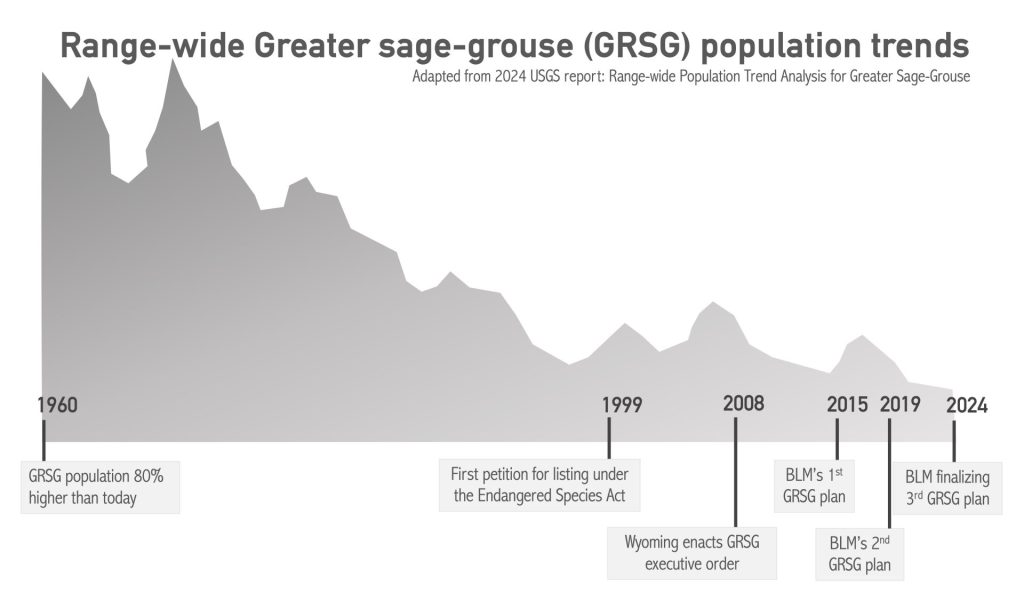
As the process leading up to this final plan has shown, there will always be competing voices saying that the BLM is using too heavy a hand, and those saying that the agency isn’t doing enough for sage-grouse. But what’s needed right now isn’t ongoing disagreement, nor delays. Research shows we’re hemorrhaging more than 1 million acres of functioning sagebrush habitat a year. Sage-grouse numbers are a sliver of what they were sixty years ago. To stem declines and retain this species on Wyoming’s wide-open landscapes, what’s needed right now is action.
With that in mind, let’s take a closer look at the plan — how we got here, what the plan does, and what we can expect looking ahead.
The long path towards a sage-grouse plan
Sage-grouse and the sagebrush steppe that sustains them are in trouble. Both have experienced steep losses, with populations of sage-grouse down 80 percent from 1965. Sage-grouse act as a bellwether for the overall health of the sagebrush ecosystem and their decline sounds the alarm for the future of these lands and the communities that depend on them. Without decisive action from the BLM to address growing threats, the bird’s habitat will be further compromised, resulting in rangewide sage-grouse population losses.
Here in Wyoming, we have been fortunate compared to other range states. Between Wyoming’s executive order that’s helped protect sage-grouse habitat with bipartisan support since 2008, climatic conditions that favor sagebrush, and a small human population, Wyoming’s sage-grouse populations have been more resilient than those in neighboring states. Nevertheless, Wyoming is not immune to the habitat loss and degradation laying siege to the Intermountain West and continued long-term declines in Wyoming are a concern. A comprehensive, West-wide sage-grouse plan from the BLM is wholly necessary and overdue.
The BLM has been trying to tackle this problem for going on 10 years. First petitioned for listing in 1999, the US Fish and Wildlife Service determined that Endangered Species Act protection for the Greater sage-grouse was warranted in 2010. This kicked off a massive effort between states and federal agencies — an effort in which Wyoming played a leading role — to create robust plans for protective management. The BLM’s first range-wide sage-grouse management plans rolled out in 2015 with strong bipartisan support from Western governors. In response to conservation measures in these 2015 plans, the USFWS determined the species no longer needed federal protection under the ESA. Unfortunately, these plans were never fully implemented as intended before the first Trump administration carried out revisions that weakened habitat protections to better favor industry. That revised plan was finalized in 2019, but was quickly blocked following litigation. Now, once again, the BLM is on the cusp of finalizing a plan for managing sage-grouse habitat. By building off the 2015 and 2019 plans, clarifying points of confusion, incorporating the latest science, and weighing input from varied stakeholders, the BLM has put forward a balanced approach to sage-grouse habitat management that honors the agency’s multiple-use mandate.
What the plan means for Wyoming
This sage-grouse plan is truly staggering in its scope and detail, as you would expect for a document that amends land use plans for over 70 BLM field offices across 10 states. For Wyoming specifically, the plan introduces some significant new protections for the bird’s habitat to ensure development and industrial uses don’t come at the expense of sage-grouse. With about 97 percent of BLM lands in Wyoming classified as sage-grouse habitat — and almost half of that considered “priority habitat” — this is a big deal! Below are some of the standout provisions that would apply to sage-grouse habitat in Wyoming under the final sage-grouse plan.
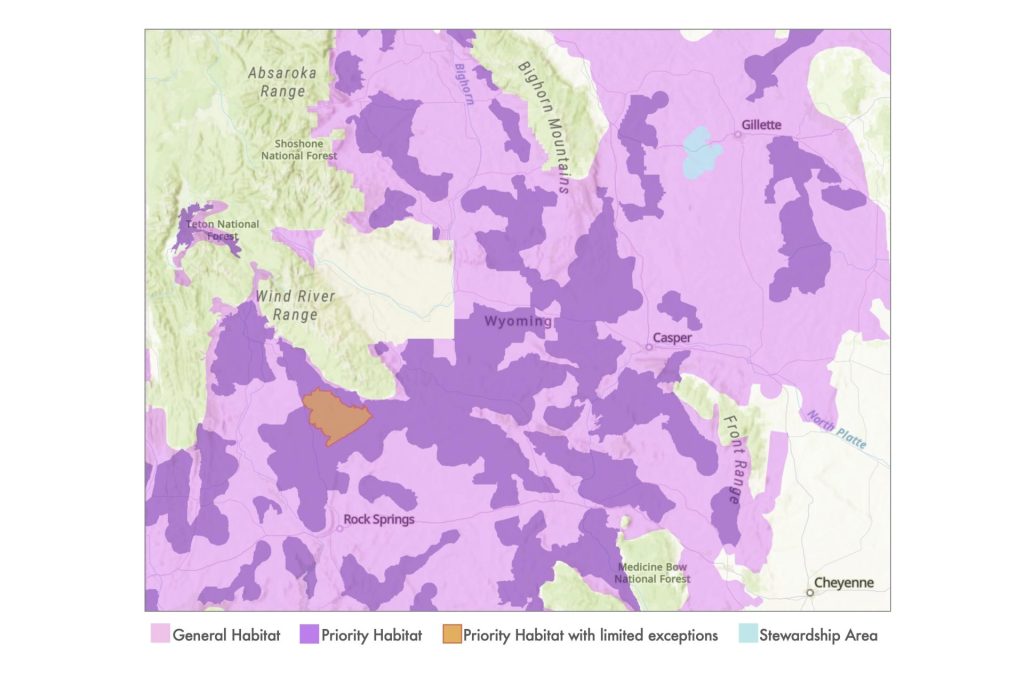
Priority Habitat Management Areas
This is the best of the best sage-grouse habitat and overlaps what the state of Wyoming has identified as sage-grouse “core area”. Just under half of the land BLM manages in Wyoming is classified as PHMA, at about 8.6 million acres. Under BLM’s latest plan, these are just some of the management guidelines that would apply in priority habitat:
- Utility-Scale Solar: excluded; some exceptions
- Utility-Scale Wind: excluded; some exceptions
- Oil and Gas Leasing: no surface occupancy; some exceptions/modifications/waivers
- Major Right of Ways: avoidance area unless specific conditions met
Priority Habitat Management Areas with Limited Exceptions
In reviewing the best available science, along with copious public comment, the BLM determined that select areas of priority habitat are of such exceptional quality and importance to sage-grouse that they warrant the highest level of protection. These are classified as “Priority Habitat Management Areas with Limited Exceptions”. One such area covering roughly 273,000 acres was identified in southwest Wyoming — the so-called “Golden Triangle,” which is home to the densest population of sage-grouse on Earth. This area overlaps the South Wind River Area of Critical Environmental Concern, or ACEC, included in the new Rock Springs Resource Management Plan, underscoring how irreplaceable this region of Wyoming is to a wide range of wildlife. The following noteworthy management guidelines would apply here:
- Utility-Scale Solar: excluded; no exceptions
- Utility-Scale Wind: excluded; no exceptions
- Oil and Gas Leasing – no surface occupancy; no exceptions, modifications, or waivers
- Major Right of Ways – excluded; some exceptions
Of note, the BLM considered designating this area and three others in Wyoming as ACECs in light of their significance for sage-grouse. However, partly in response to concerns voiced by Gov. Gordon, the BLM eliminated all ACECs from the latest proposed management approach we have before us.
Adaptive Management
The BLM is taking steps to standardize how it adapts management approaches when habitat and population measures dip too much, too quickly. The monitoring methods identified to inform this adaptive management, such as the Habitat Assessment Framework and Targeted Annual Warning System, are intended to create a consistent, rangewide system that catches problems before they snowball out of control. Engagement by the states in this process — especially through the free sharing of data — is critical. As the wildlife professionals responsible for sage-grouse management, each state game and fish agency oversees lek counts in the spring to gauge population levels. Having Wyoming and other states participate meaningfully is for the collective benefit of understanding how the bird is doing across its range and will allow closer examination of circumstances on the ground when areas of concern are flagged.
Where do we go from here?
Additional review of the plan is required between now and January, when a “Record of Decision” could be issued and the plan can take effect. This includes a 30-day protest period for the public and a 60-day consistency review carried out by Governors in affected range states. The BLM has signaled its commitment to getting this plan finalized expeditiously, but time is in very short supply.

After years of setbacks, it is tantalizing to see so many positive conservation measures enshrined in BLM’s new proposed sage-grouse plan. As sagebrush country faces growing threats — including a quick-moving onslaught of invasive annual grasses that cause more frequent, larger, and hotter wildfires — the time for inaction is gone. Here in Wyoming, where the health of private and public lands are intertwined and vital to the future of our communities, the benefits of smart, protective management on our public lands are far-reaching.
Unfortunately, as is the case for several actions taken in these final months of the Biden Administration, Trump’s ascendency in Washington threatens to undo a lot of this good work. Whether we see attempts to scrap the plan outright, aggressive lawsuits from multiple corners, or yet another plan rewrite, we can be sure of attacks on what the BLM has put forward. We will do all we can to push for science-based solutions and support sage-grouse conservation in the coming storm and seek allies anywhere we can find them. Neither these birds, nor the hundreds of other species they share the sagebrush biome with, have the luxury or capacity to despair in the face of mounting threats and dwindling habitat. They merely soldier on with an inextinguishable will to survive. It is up to us to do right by them and keep fighting on their behalf.
Banner image: Bob Wick, BLM

















